Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Okumura, Susumu; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Kurashima, Satoshi; Yoshida, Kenichi; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro; Ishibori, Ikuo; Agematsu, Takashi; Nara, Takayuki; Nakamura, Yoshiteru; Arakawa, Kazuo
Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Cyclotrons and Their Applications (CYCLOTRONS 2004), p.410 - 412, 2005/00
A simple analyzing system has been developed to measure the energy spread of the beam extracted from the JAERI AVF cyclotron with an energy resolution of dE/E = 0.001%. The high analyzing power can be obtained with an existing deflecting magnet system in the transport line by installing three sets of slits with a minimum width of 0.01 mm and a beam intensity monitor with a Faraday cup and semiconductor detectors. These new instruments have been compactly designed to fulfill the geometrical condition of the existing beam diagnostic chambers, which are located at the object and image positions. Installation of the analyzing system was completed and a preliminary test has been carried out. This system will be used for optimization of the flat-top acceleration system to achieve the energy spread of dE/E = 0.02%, required for microbeam production.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Yamagishi, Hideshi; Masaoka, Sei; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aizawa, Kazuya
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 529(1-3), p.336 - 341, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.85(Instruments & Instrumentation)A microstrip gas chamber (MSGC) with a capability of track discrimination for neutron detection was developed whilst ensuring the stability of the MSGC and fulfilling the specifications required for detectors using in high-flux reactors and high-intensity pulsed-neutron sources. The developed two-dimensional detector system comprises a MSGC with individual signal channel read-outs and a new instrument system with a capability of secondary-particle discrimination (InSPaD). The InSPaD identifies the particles -proton and triton- created in the nuclear reaction 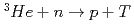 by a simple, fast and cost-effective method using the difference in the track length, and it enables a small amount of heavy gas such as
by a simple, fast and cost-effective method using the difference in the track length, and it enables a small amount of heavy gas such as 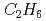 with helium-3 to be used as the filling gas whilst achieving a high spatial resolution.
with helium-3 to be used as the filling gas whilst achieving a high spatial resolution.
Saito, Yuji; Nakatani, Takeshi*; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Agui, Akane; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Yokoya, Akinari
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 474(3), p.253 - 258, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:76 Percentile:97.53(Instruments & Instrumentation)The present performance of a soft X-ray bealmine BL23SU at SPring-8 is described. The resolving power realized on a varied-line-spacing plane grating monochromator connected to a was estimated to be better than 10000 at 400 eV and 6500 at 867 eV. In addition, reasonable photon flux of more than 10 photons/sec/100mA/0.02% b.w. is available in the energy range of 0.5-1.8 keV at experimental stations.
photons/sec/100mA/0.02% b.w. is available in the energy range of 0.5-1.8 keV at experimental stations.
; ; Ohara, Yoshihiro; *; *
Review of Scientific Instruments, 50(5), p.1111 - 1113, 1985/00
no abstracts in English
*;
JAERI-M 8425, 31 Pages, 1979/09
no abstracts in English
JAERI-M 8327, 55 Pages, 1979/07
no abstracts in English
Asai, Masato; Ishibashi, Yuichi*; Niwase, Toshitaka*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Ito, Yuta; Sato, Tetsuya; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sakaguchi, Satoshi*; Morita, Kosuke*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
Solar cells for power generation can be used as a high-energy heavy-ion detector because it has diode characteristics. To utilize the solar cells for fission-fragment measurements, we have investigated the response (energy resolution and pulse height defect) of a solar cell to heavy ions of various nuclides with several different energies.